1 Principles of chemistry
2 Inorganic chemistry
3 Physical chemistry
4 Organic chemistry
1 Principles of chemistry
(d) The Periodic Table
Students should:
1.18 understand how elements are arranged in the Periodic Table:
• in order of atomic number
• in groups and periods.
1.19 understand how to deduce the electronic configurations of the first 20 elements from
their positions in the Periodic Table
1.20 understand how to use electrical conductivity and the acid-base character of oxides to
classify elements as metals or non-metals
1.21 identify an element as a metal or a non-metal according to its position in the Periodic
Table
1.22 understand how the electronic configuration of a main group element is related to its
position in the Periodic Table
Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Chemistry –
Specification – Issue 2 – April 2018 © Pearson Education Limited 2018
13
Students should:
1.23 understand why elements in the same group of the Periodic Table have similar
chemical properties
1.24 understand why the noble gases (Group 0) do not readily react
Notes:
1/2
1.18: Understand How Elements are Arranged in the Periodic Table: In Order of Atomic Number, In Groups and Periods
PERIOD: Horizontal Rows that Show the Number of Shells of Electrons an Atom Has
GROUP: Vertical Columns that Show How Many Outer Electrons an Atom Has
THE PERIODIC TABLE: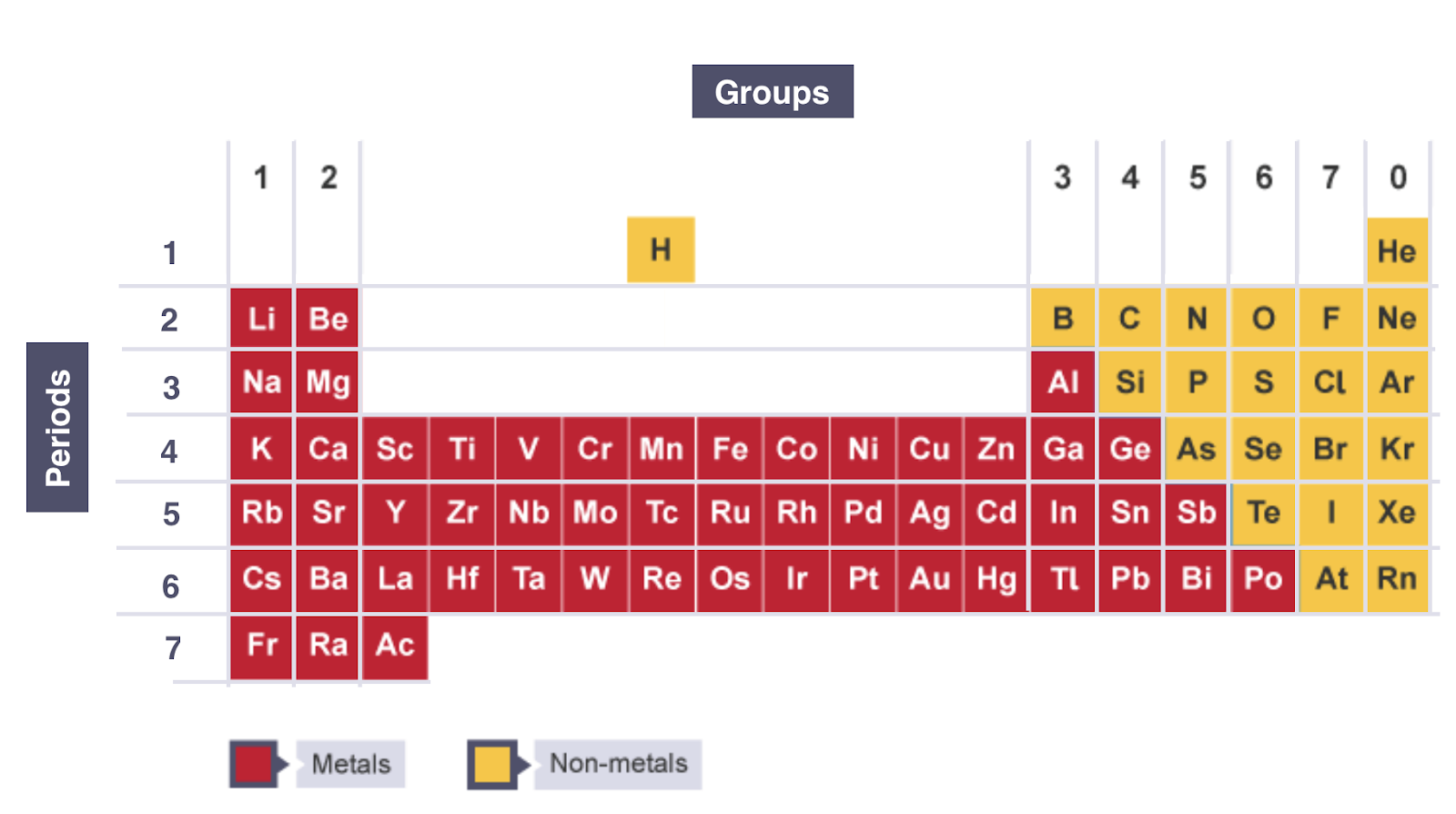
All Elements are Arranged in the Order of Increasing Atomic Number from Left to Right
1.19: Understand How to Deduce the Electronic Configuration of the First 20 Elements from their Positions in the Periodic Table
ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION: The Arrangement of Electrons into Shells for an Atom
s- Electrons Always Occupy Shells that are Closest to the Nucleus First
- When a Shell Becomes Full, Electrons will Fill the Next Shell
ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION OF FIRST 20 ELEMENTS:
ELEMENT
|
NUMBER OF ELECTRONS
|
ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION
|
HYDROGEN
|
1
|
1
|
HELIUM
|
2
|
2
|
LITHIUM
|
3
|
2 . 1
|
BERYLLIUM
|
4
|
2 . 2
|
BORON
|
5
|
2 . 3
|
CARBON
|
6
|
2 . 4
|
NITROGEN
|
7
|
2 . 5
|
OXYGEN
|
8
|
2 . 6
|
FLUORINE
|
9
|
2 . 7
|
NEON
|
10
|
2 . 8
|
SODIUM
|
11
|
2 . 8 . 1
|
MAGNESIUM
|
12
|
2 . 8 . 2
|
ALUMINIUM
|
13
|
2 . 8 . 3
|
SILICON
|
14
|
2 . 8 . 4
|
PHOSPHORUS
|
15
|
2 . 8 . 5
|
SULFUR
|
16
|
2 . 8 . 6
|
CHLORINE
|
17
|
2 . 8, . 7
|
ARGON
|
18
|
2 . 8 . 8
|
POTASSIUM
|
19
|
2 . 8 . 8 . 1
|
CALCIUM
|
20
|
2 . 8 . 8 . 2
|
1.20: Understand How to Use Electrical Conductivity and the Acid-Base Character of Oxides to Classify Elements as Metals or Non-Metals
METALS
|
NON - METALS
|
Basic Oxides (Alkaline)
|
Acidic Oxides (Acidic)
|
Good Conductors of Electricity
|
Poor Conductors of Electricity
|
High Melting and Boiling Point
|
Low Melting and Boiling Point
|
Malleable
|
Flaky
|
1.21: Identify an Element as a Metal or a Non-Metal According to its Position in the Periodic Table
THE PERIODIC TABLE:
A Zig - Zag Line in this Diagram Separates the Metals on the Left, from the Non - Metals on the Right
1.22: Understand How the Electronic Configuration of a Main Group Element is Related to its Position in the Periodic Table
ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION: The Arrangement of Electrons into Shells for an Atom (E.g Electronic Configuration of Carbon is 2 . 4 )
s
ELECTRONIC CONFIGURATION AND POSITION IN PERIODIC TABLE
s- The Number of Notations in the Electronic Configuration will show the Number of Shells of Electrons the Atom has, Showing the Period
- The Last Notation Shows the Number of Outer Electrons the Atom has, Showing the Group
EXAMPLE: Electronic Configuration of Chlorine:
PERIOD: The Red Numbers at the Bottom Show the Number of Notations which is 3, Showing that a Chlorine Atom has 3 Shells of Electrons
GROUP: The Green Box Highlights the Last Notation which is 7, Showing that a Chlorine Atom has 7 Outer Electrons
ON THE PERIODIC TABLE: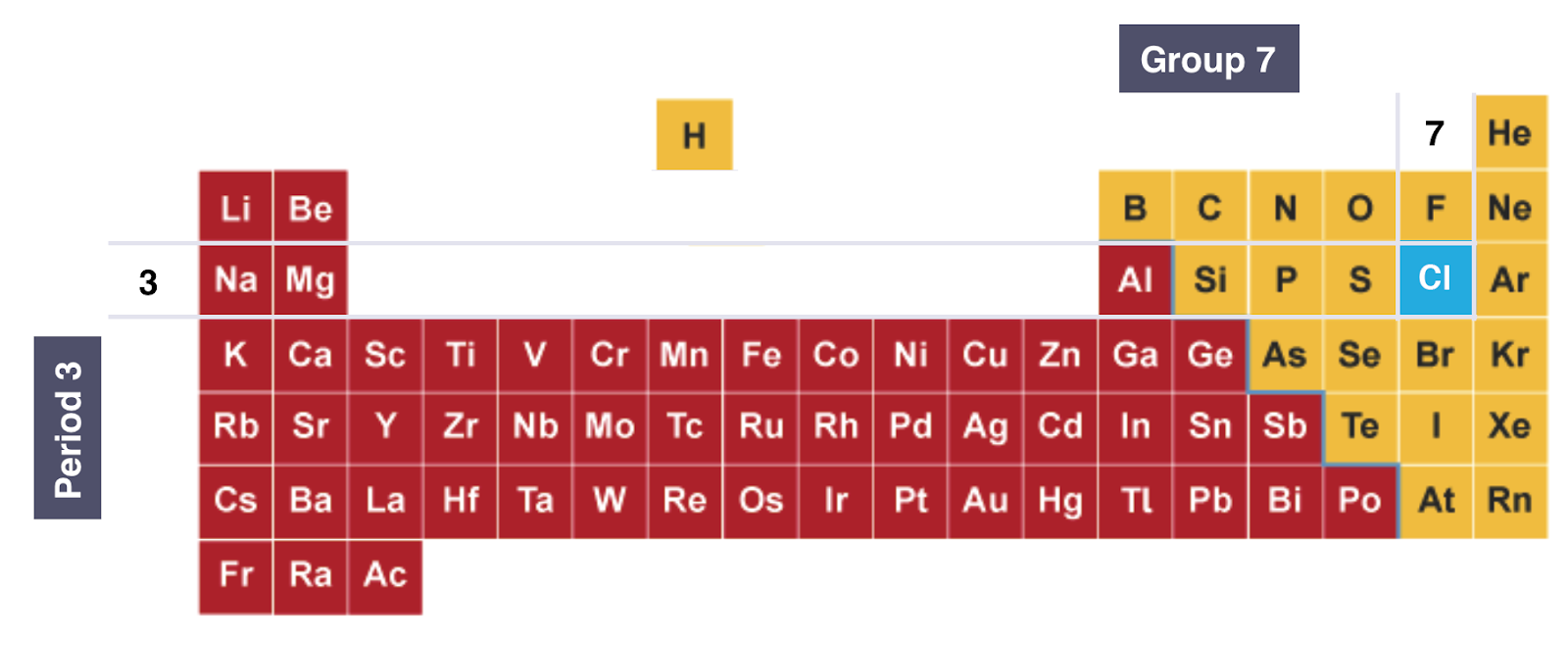
Diagram Showing the Position of Chlorine on the Periodic Table
1.23: Understand Why Elements in the Same Group of the Periodic Table have Similar Chemical Properties
GROUP: Vertical Columns that Show How Many Outer Electrons an Atom Has
s
CHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF ELEMENTS IN THE SAME GROUP:
s- Elements in the Same Group in the Periodic Table will have Similar Chemical Properties
- This is because they have the Same Number of Outer Electrons so will React and Bond Similarly
- For Example, Both Lithium and Sodium are in Group 1 and can React with Elements in Group 7 to Form an Ionic Compound (Charges of Group 1 Elements are +1, Charges of Group 7 Elements are -1)
Book online tuition for modern periodic Table at Ziyyara for all boards. Taking Home tuition classes for Chemistry can save your time. Also it is more engaging and convenient. You don't need to hurry for the classes. Online tuitions are flexible as there are multiple slots available and you can schedule your online classes as per your availability.
ReplyDeleteFor more details or Book free Demo class call on +919654271931
Visit us :- https://ziyyara.in/blog/modern-periodic-classification-of-elements.html